
Expanded Polystyrene (EPS), commonly known as Styrofoam, is one such material that has garnered attention due to its recyclability.
Expanded polystyrene (EPS) is a rigid, white, closed-cell foam plastic material made from solid polystyrene beads that contain an expansion gas.
The densified EPS can be transformed. It may be ground up, melted, pulled into strands and cut into tiny pellets, which are then used to make picture frames and clothes hangers.
Recycled EPS is also sometimes used in construction, making composite building materials and architectural moldings.
Understanding EPS and Its Recycling Process
What is EPS?

Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) is a lightweight, rigid, and closed-cell foam. It is widely used for packaging, insulation, and various consumer products due to its excellent insulating properties and impact resistance. EPS is composed of 98% air and 2% polystyrene, making it a low-density material that is easy to handle.
The Recycling Process of EPS
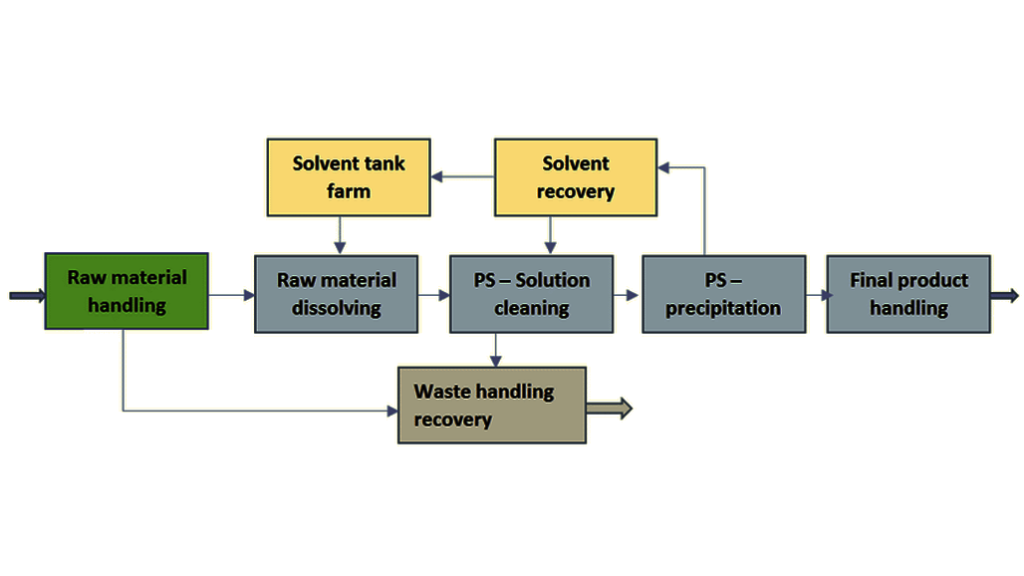
Recycling EPS involves several steps:
- Collection: EPS waste is collected from various sources, including packaging, construction sites, and consumer goods.
- Sorting and Cleaning: The collected EPS is sorted to remove contaminants and ensure purity.
- Shredding: The clean EPS is then shredded into smaller pieces to facilitate further processing.
- Melting and Extrusion: The shredded EPS is melted and extruded into pellets or other usable forms. This step often involves the addition of stabilizers to enhance the material’s properties.
- Reformation : The extruded EPS pellets can be reformed into new products, including components for mold making.
Properties of Recycled EPS

Physical Properties
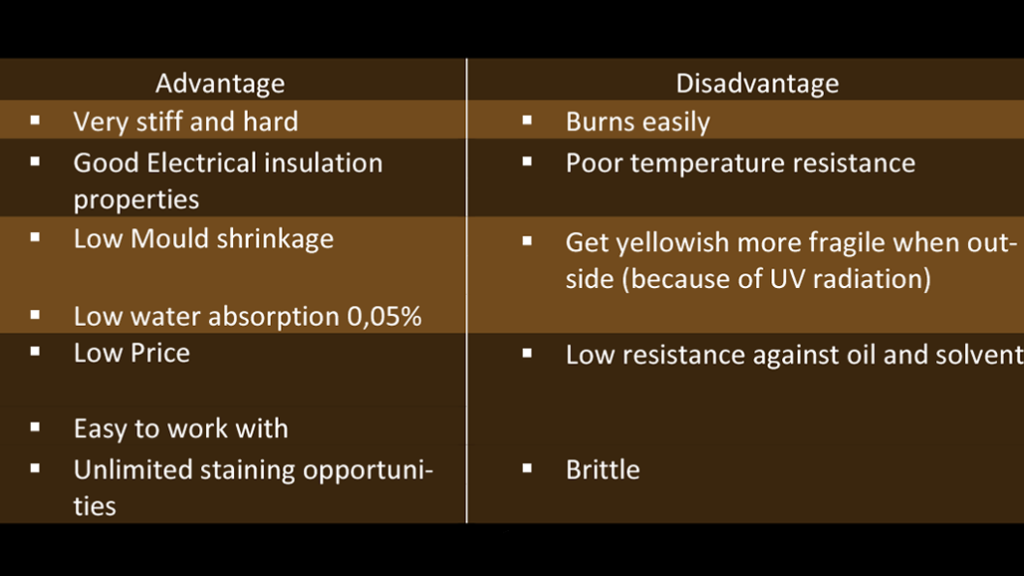
Recycled EPS retains many of the physical properties of virgin EPS, including:
– Lightweight: Due to its high air content, recycled EPS is extremely light, which is advantageous in mold making.
– Insulating: It has excellent thermal insulation properties, which can be beneficial in certain mold-making applications.
– Impact Resistance: EPS provides good shock absorption, making it durable under various conditions.
Mechanical Properties
– Compressive Strength : Recycled EPS offers considerable compressive strength, which is crucial for mold making, particularly in applications requiring dimensional stability.
– Flexural Strength : It also exhibits good flexural strength, allowing it to withstand bending forces during the molding process.
Chemical Resistance
EPS is resistant to many chemicals, including water and most solvents, ensuring durability and longevity in mold making applications.
Advantages of Using Recycled EPS in Mold Making
Environmental Benefits
1. Reduces Landfill Waste : Utilizing recycled EPS diverts waste from landfills, addressing the environmental concern of EPS waste accumulation.
2. Conserves Resources : Recycling EPS conserves the petroleum resources used to produce virgin polystyrene, promoting a more sustainable use of materials.
3. Lower Carbon Footprint : The energy required to recycle EPS is significantly lower than that needed to produce new EPS, resulting in a reduced carbon footprint.
Economic Benefits
- Cost-Effective : Recycled EPS is generally less expensive than virgin EPS, offering cost savings in material procurement.
- Energy Savings : The reduced energy consumption in recycling processes translates to lower operational costs.
Performance Benefits
- Consistent Quality : Modern recycling techniques ensure that the quality of recycled EPS is comparable to that of virgin EPS, providing reliable performance in mold making.
- Customizability : Recycled EPS can be tailored to meet specific requirements of different mold making applications, enhancing its versatility.
Challenges of Using Recycled EPS in Mold Making
Contamination
One of the primary challenges in using recycled EPS is contamination. Impurities in the recycled material can affect its quality and performance. Ensuring thorough cleaning and sorting processes is essential to mitigate this issue.
Consistency
Achieving consistent quality in recycled EPS can be challenging due to variations in the feedstock. Standardizing the recycling process and maintaining strict quality control measures are crucial for producing reliable recycled EPS.
Mechanical Properties
While recycled EPS retains many of the properties of virgin EPS, there can be slight differences in mechanical properties such as compressive and flexural strength. These variations need to be accounted for in the mold design and application.
Market Acceptance
The use of recycled materials in industrial applications can sometimes face resistance due to perceived quality issues. Educating stakeholders about the benefits and capabilities of recycled EPS is essential to increase its adoption in mold making.
Applications of Recycled EPS in Mold Making
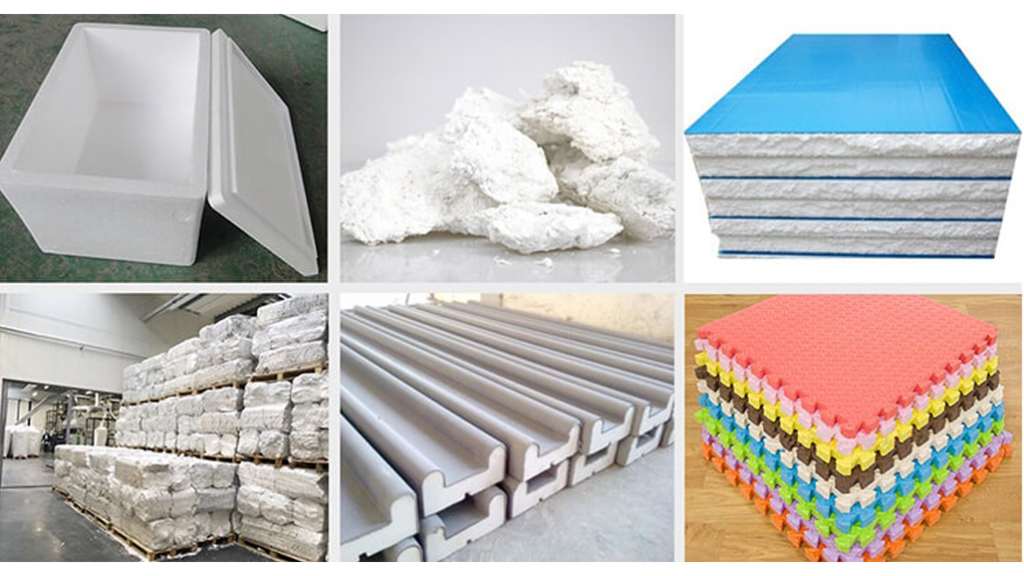

Prototyping
Recycled EPS is ideal for prototyping due to its ease of shaping and low cost. It allows designers to create and test molds quickly and economically.
Lost Foam Casting
In lost foam casting, a foam pattern is used to create a mold. Recycled EPS is perfect for this process as it can be easily shaped into complex patterns and vaporizes cleanly during casting, leaving behind a precise mold cavity.
Insulation Molds
Recycled EPS can be used to create molds for producing insulation products. Its excellent thermal properties make it suitable for this application, ensuring the insulation products meet required standards.
Packaging Molds
The use of recycled EPS in making molds for packaging materials leverages its shock-absorbing properties, ensuring that the packaging products provide adequate protection for fragile items.
Art and Sculptures
Artists and sculptors can use recycled EPS to create molds for intricate designs. Its lightweight nature and ease of manipulation make it an attractive option for creative projects.
Conclusion
The use of recycled EPS in mold making presents a promising avenue for enhancing sustainability while maintaining high standards of performance and cost-effectiveness.
Despite challenges such as contamination and consistency, advancements in recycling technology and increased market acceptance are paving the way for broader adoption.
Through detailed case studies and future prospects, it is evident that recycled EPS has significant potential in various mold making applications.
As industries continue to prioritize environmental responsibility, recycled EPS will likely play an increasingly important role in shaping a sustainable future.
By integrating recycled EPS into mold making processes, companies can reduce their environmental impact, lower costs, and contribute to a circular economy.
This approach not only addresses the pressing issue of EPS waste but also demonstrates the viability and benefits of using recycled materials in industrial applications.
As we move towards a more sustainable future, the role of recycled EPS in mold making is set to become ever more critical, offering a practical solution to some of the industry’s most pressing challenges.
